In this article of today, we are going to see how to generate random numbers using any of the following methods:
- Generating a random number
- Generating a random float and integer
- Generating random number arrays
- Generating random number from an array
What is a random number?
This is a number which cannot be predicted before its occurrence. This number might not different every time.
Programmatically, they are two categories of random numbers:
- Pseudo-Random numbers
- True Random numbers.
Just as programs which are written by programmers are a set of instructions, we must follow an algorithm to generate random numbers.
Random numbers which are generated using an algorithm are called Pseudo-Random numbers. To generate a true random number, it is important to get the data from sources such as the keyboards, mouse activities, etc.
In this article of today, we are concerned only the Pseudo-Random numbers using NumPy
Generating a random NumPy module/number
NumPy library has a random module which can be used to generate numbers.
from numpy import random
Following the instructions of the randint method, the compiler returns the output as a number between 0 and 80. That is the randint() method is used to generate a number between a given range.
OUTPUT
Generating a float
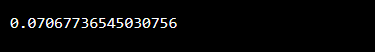
just as with the case above, we are going to use the rand() method to generate a float. This method returns a random float between 0 and 1.
Example
from numpy import random
OUTPUT
Generating random number arrays
Just like with the two examples above, we can also the randit() and rand() method to generate random number array. To use these methods this case, we are going to be more specific, that is we are going to specify the shape of the array.
- Generating integers using randit()method
we are going to specify the size of the array
from numpy import random
The size being specified, the compiler returns an array of 4 random numbers.
OUTPUT
- Generating a 2-D array
from numpy import random
OUTPUT
- Generating a float
We are going to use the rand() method
from numpy import random
OUTPUT
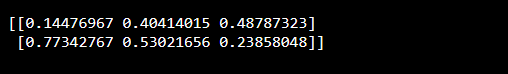
Generating a 2-D array float
Example
from numpy import random
OUTPUT
Generating Random Number from an Array
We are going to use a method called the choice() method to randomly select a value from a given array.
Example
from numpy import random
The compiler randomly selects a value from the given array.
OUTPUT
Generating a 2-D array using the choice()method
This is possible if we add a specific size to the array to be generated.
Example
from numpy import random
A specific size has been given for the array to be created. The compiler generates an array randomly according to this size.
OUTPUT
Take note that the output changes every time the program is executed. Hope this article was very exciting. If so, stay tune on the platform to get more knowledge on NumPy and other programming languages. Have a time coding.







Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.